In this blog you are going to learn, what is management, importance of management, objectives of management, functions of management and levels of management.

What is Management ?
Management is the process of planning and organizing, leading and controlling a company’s resources, operations, and workflow in order to achieve certain goals as effectively and efficiently as feasible.
Management is the backbone of any successful organisation. Either you are managing a small team, a startup, or a large organization knowing the fundamental of Management is essential to reaching objectives successfully and economically.
In simple terms we can say that Management ensures that the work is done effectively, and on time.
Efficiency in management refers to the ability to complete things correctly and at a low cost. Management effectiveness is defined as completing tasks within set time frames to produce real benefits.
Importance of Management
1. Management Helps to Achieve Goals
Management arranges production variables, assembles and organizes resources, and integrates them effectively to meet goals. It focuses group efforts towards achieving predetermined goals.
Managers contribute to the achievement of organizational goals. Managers define an organization’s vision and strategy, and they manage resources and people to achieve those objectives. Managers are also accountable for hiring qualified team members who can take on tasks for the organization.
2. Maintain an Efficient Work Culture
A positive atmosphere at work is one in which employees are motivated and proud to be a part of the firm.
Managers promote an efficient work environment and ensuring that all employees have access to the tools they need, such as equipment or software, to complete their responsibilities efficiently.
3. Cost Reduction
Cost reduction is a critical task that highlights the value of strategic management.
Managers are in charge of production costs, which include both people and overhead expenses such as office supplies and utility bills. Managers typically do not have direct control over these types of expenses; nevertheless, they can affect them through a variety of measures, including staff training and policy changes.
In addition to minimizing operating costs by eliminating needless expenses such as paperclips or idle office space, they must constantly evaluate financial performance in order to discover areas where efficiency may be improved.
4. Ensuring Long-term Growth
Management ensures long term growth of an organisation.
Managers are in charge of generating new ideas, putting those ideas into action, and assisting the organization in its growth. They must also ensure that employees have a clear knowledge of their employment objectives, which will allow them to attain their maximum potential.
5. Organisational Stability
Management promotes organisational Stability through efficient planning and control procedures. Strategic planning allows managers to anticipate probable obstacles,set Clear targets.
By proactively resolving difficulties and aligning resources with organisational goals, management creates a stable environment in which the business may prosper, especially in the face of external or internal uncertainties.
Characteristics of Management
1. Goals Oriented Process
Management focuses on achieving organisational objectives by directing individual efforts towards common goals. Management ensures that all actions supports the organisation objective.
2. Pervasive
Management pto all types of organisations such as social, economic,or political, and at all levels from top executives to frontline managers.
3. Continuous Process
Management is a continuous sequence of interrelated responsibilities such as , planning, organising, staffing, directing and controlling that are undertaken on a constant basis to adapt to changing situations.
4. Dynamic Function
Management must adapt to the ever changing external environment, which includes social, economic and political aspects,in order to assure organisation success.
5. Group Activity
It involves organising the efforts of a group of people,recognising that cooperation and collaboration are important to attaining organisational goals.
6. Intangible
While management is not visible,it’s presence is felt through an organisation’s efficient and successful operation, which leads to goal achivement.
7. Multidimensional
Management is responsible for overseeing and supervising a company’s or organization’s service or production cycle. Managers guide and collaborate closely with their team members. A manager views a staff member as both an individual with varying requirements and a member of a bigger group. To be effective, managers must persuade their team members to use their unique strengths to help the organization achieve its objectives.
Objectives of Management
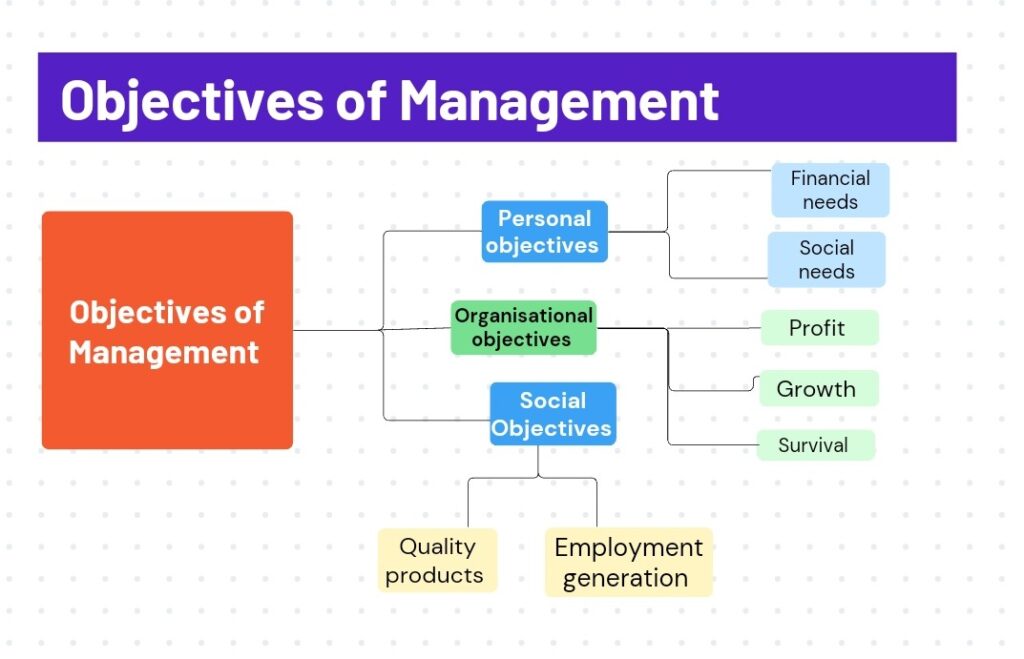
Organisational Objectives
Management is responsible for setting and achieving the company’s objectives. It must meet a variety of objectives in all activities while considering the interests of all owners, including stakeholders, consumers, the government, and employees.
The primary goal of any corporation must be to maximize the potential advantage of its material and human resources, to achieve the firm’s financial objectives.
And they are –
- Survival: The primary objective of any organisation is survival. Management must make every effort to ensure the business’s continued operation. To survive ,an organisation must generate enough revenue to cover it’s expenses.
- Profit: Poor survival is insufficient for an organisation.Management has to ensure that the company makes a profit. Profit is an important catalyst for the firm’s long-term prosperity. Profit is critical for covering the costs and uncertainties of the firm.
- Growth: A company must increase its chances in the long run, which demands the concern to develop. To succeed in business, managers must fully understand the firm’s growth potential.
Personal Objectives
Personal objectives of management focuses on fulfilling the needs of employees within an organisation.
These objectives are related to the development of employees working in an organisation. Some of these objectives include:
- Financial needs, Providing competitive pay and benefits.
- Social needs, Self-esteem,per recognition,and respect for coworkers.
Social Objectives
It involves establishing benefits for the society. As a member of the community, every business, whether trading or non-trading, has a social responsibility to fulfill.
This refers to continually creating financial value for many aspects of society. This involves adopting environmentally friendly production technology, providing job chances for underprivileged members of the community, and providing primary facilities such as crèches and schools to employees.
These objectives are –
- Using environment-friendly methods of production.
- Producing quality products at reasonable rates.
- Employment generation in society.
Functions of Management
1. Planning
Planning involve creating a timeline of tasks that must be completed to achieve a given goal. Managers implement plans.
Planning should be done in a systematic manner to avoid wasting resources and time. A precise plan of action reduce confusion,risk,waste,and ambiguity.
For example –
A small business’s top management may set a high sales target for one quarter to make up for losses in the preceding quarter.
The founder of a start-up may intend to make official efforts to collaborate with the government and other significant institutions in order to scale up their operations. Local digital marketing company leaders may intend to expand their product and service offerings into the international market.
2. Staffing
Staffing involves recruiting and developing a staff for the organization. Companies’ hiring processes are frequently time-consuming and thorough.
Management establishes professional responsibilities inside the organization and the skills/qualities required to excel in these jobs. The manager then picks candidates for those positions through the recruitment process. Candidates are trained and then hired by the company once they have been selected.
Managers are also in charge of issuing appraisals and promotions as part of the personnel process.
Staffing ensures that the organisation has right people in right position.
Example –
Recruiting skilled developers for a software company.
3. Organising
Organizing defines roles, duties, and workflows to guarantee that activities are completed efficiently. As an example, assign team members to specific tasks based on their skills.
The goal of organisation is to promote a mutually beneficial interaction between the company’s personnel, financial, and physical resources.
Proper organisation gives a plan of action that meets all success criteria. Organizing includes identifying and categorizing corporate operations, as well as delegating and coordination.
For example –
Top management may distribute finances or resources to various branches. The branch managers must then distribute funding to departments within the branch based on their operating needs. The department heads then keep track of the monies’ daily expenditures.
4. Directing
Directing involves taking the necessary actions to set work in motion and maintain productivity in order to achieve organizational objectives.
Excellent leadership, communication, and interpersonal skills are required to motivate the team to achieve organizational goals.
A manager’s primary responsibilities include supervising, inspiring, and leading staff workers.
For example –
Motivating the sales team to meet quarterly targets through prizes and recognition.
5. Controlling
Business operate in accordance with certain performance requirements. A manager ensures that the staff’s total production matches the company’s quantity and quality requirements.
Each level of control prohibits total divergence from the quality criteria that were established.
Controlling involves monitoring progress, identifying deviations from the plan,and implementing corrective actions.
For example –
Analyzing project timelines and addressing delays promptly.
Levels of Management
There are three levels of management. These are –
- Top level of management
- Middle level of management
- Lower level of management
1. Top Level of Management
Top level of management,comprises of a board of directors, a CEO, or a managing director.
Top management is the ultimate source of authority, managing an enterprise’s goals and policies. It focuses more on planning and coordinating functions.
The function of top management are as follows:
- Top management establishes the enterprise’s general policies and objectives.
- It provides the necessary instructions for the production of department budgets, processes, schedules, and other documents.
- It develops strategic plans and policies for the enterprise.
- It appoints executives for middle-level positions, such as departmental managers.
- It controls and coordinates the activity of all departments.
- It is also responsible for maintaining communication with the outside world.
2. Middle Level of Management
The middle level consists of branch managers and departmental managers. They are accountable to the senior management for the operation of their department.
They spend more effort on organizational and directing functions. Small organizations have only one layer of middle management, but large firms may have senior and junior middle management.
The role of middle level management as follows:
- Middle level management carry out the organization’s strategies in accordance with top-level management rules and directions.
- They establish plans for the organization’s sub-units.
- They assist in the employment training of lower-level managers.
- They understand and explain policies from high management to lower levels.
- They are in charge of coordinating all activities within the division or department.
- It also delivers vital reports and data to upper management.
- They evaluate the performance of junior managers.
- They are also accountable for inspiring lower-level managers to perform better.
3. Lower Level of Managment
The lower level of management is also known as the supervisory or operational level. It is made up of supervisors, foremen, section officers, and a superintendent.
“Supervisory management refers to those executives whose work has to be largely with personal oversight and direction of operative employees” . In other words, they are concerned with the direction and control functions of management.
Activities of below level management are as follows:
- They assist in resolving employee grievances.
- They supervise and guide the subordinates.
- They are in charge of delivering training to employees.
- They arrange for the supplies, machines, and tools required to complete the tasks at hand.
- They prepare periodic reports on the workers’ performance.
- They maintain organizational discipline.
- They advise and instruct workers in their daily activities.
- They are accountable for both the quality and quantity of production.
- They are also responsible for maintaining strong relationships within the organization.
FAQ
What is the definition of management ?
Management is the process of planning and organizing, leading and controlling a company’s resources, operations, and workflow in order to achieve certain goals as effectively and efficiently as feasible.
Who is the father of management ?
Henri Fayol is known as the father of modern management for developing the 14 principles of management.
What are the levels of management?
There are three levels of management. These are –
Top level of management,
Middle level of management, Below level of management.
